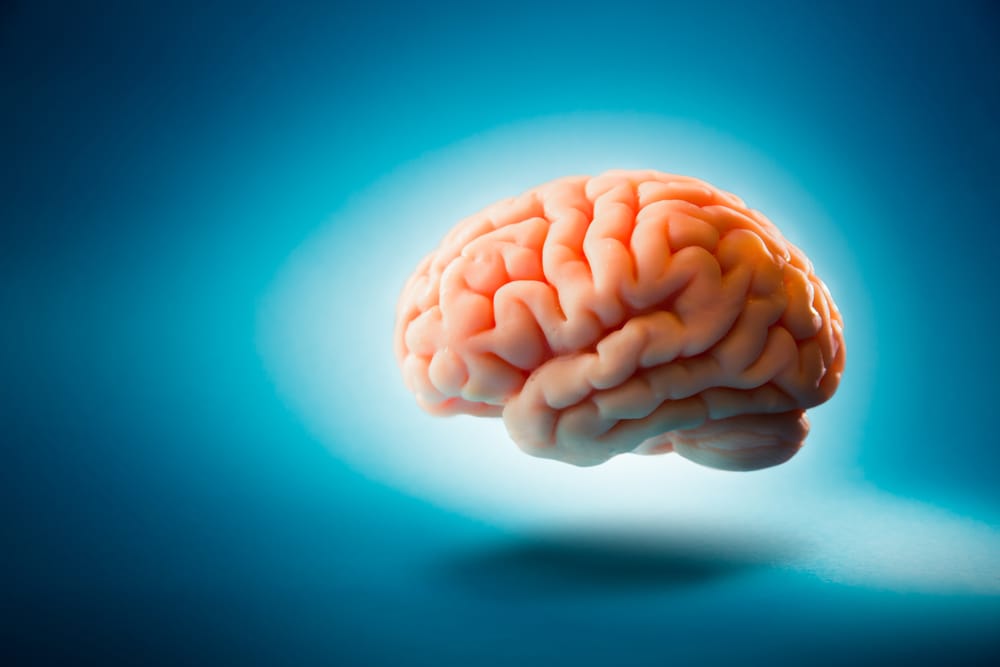
The Circle of Willis is a ring-like arterial structure located at the base of the brain that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures. It is a component of the cerebral circulation and is comprised of five arteries.
Even if biology has never been your favorite subject, you still probably know a few basic things about the human body, including the fact that the heart pumps blood to the entire body, the stomach helps in digestion, the lungs allow us to breathe, and of course, the brain makes sure that every organ in the body works the way it’s designed.
There is no denying that the human brain performs some of the most critical functions to run the body. Needless to say, it’s arguably the most complicated organ we have discovered among all living beings. Yet, no matter how smart and sophisticated it may be, at the end of the day, it’s just an organ within the human body, just like all the rest.
The ‘smartest’ part of the body.(Photo Credit : Fer Gregory / Shutterstock)<a name=\'more\'></a>
Having said that, the brain also relies on a number of smaller nuts and bolts to keep it running. One of those small, relatively unknown parts is the Circle of Willis. In this article, we shall discuss its anatomy and importance to the brain and its surrounding structures.
What is the Circle of Willis?
The Circle of Willis (often abbreviated as CW or CoW) is a structure located inside the head (around eye level) that provides a blood supply to the brain and neighboring structures.
More specifically, it’s a circulatory anastomosis (i.e., a connection between two blood vessels, such as between arteries, veins, or between an artery and a vein (arterio-venous anastomosis)) that encircles the stalk of the pituitary gland and allows distribution of blood to the brain and nearby structures.
The Circle of Willis gets its name from Thomas Willis, an eminent English physician, who described the arterial ring present at the base of the brain 400 years ago.
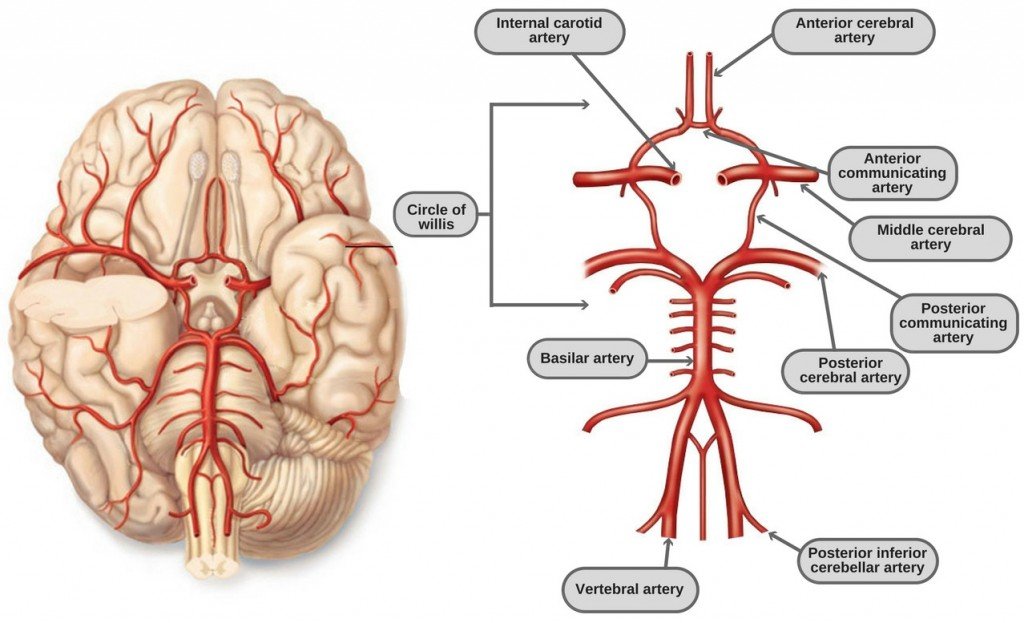
Circle of Willis anatomy
Also referred to as the Loop of Willis, the cerebral arterial circle or the Willis polygon, it is composed of five main arteries:
Internal carotid artery (left and right)
Anterior cerebral artery (left and right)
Anterior communicating artery
Posterior cerebral artery (left and right)
Posterior communicating artery (left and right)
The CoW encircles the pituitary stalk, optic tracts and basal hypothalamus. It must be noted that anatomically, the CoW is not the same in every individual; it is found to have anomalies in nearly 50% of people (Source).
Circle of Willis functions
The Circle of Willis is basically an arrangement of interconnected vascular channels that ensure that the (oxygenated) blood flow to the brain continues unimpeded, in case any of the principal suppliers are obstructed by injury, physical pressure or disease.
(Photo Credit : OpenStax College / Wikimedia Commons)
To be more specific, biologically, it’s said that the CoW creates a redundancy for collateral circulation in cerebral circulation. For the uninitiated, collateral circulation is simply the flow of blood through an alternate route around an obstructed vein or artery, which is made possible by neighboring minor vessels.
Due to the presence of the CoW, if one of the vessels supplying blood to the brain is narrowed or blocked completely, the other vessels can preserve the cerebral perfusion pressure (i.e., the net pressure gradient causing cerebral blood flow to the brain) well enough to prevent the onset of a condition called ischemia (i.e., restriction of blood supply to tissues).
In a nutshell, the Circle of Willis acts as a safety valve for the brain and makes sure that it sits comfortably at the top, without having to worry about any blood supply issues.
 https://archive.janatna.com/
https://archive.janatna.com/



 https://archive.janatna.com/
https://archive.janatna.com/